Proximal Femur Nail Antirotation (PFNA): Advancements in Femoral Fracture Fixation
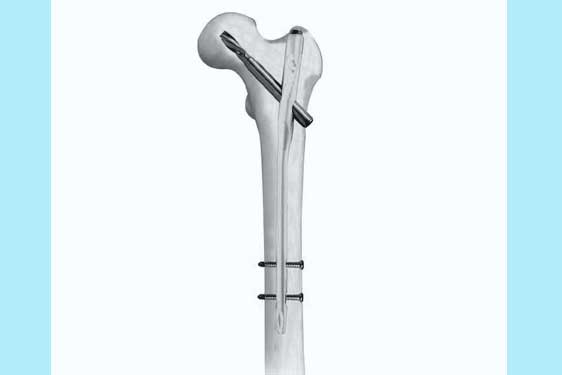
Proximal Femur Nail Antirotation (PFNA)
Femoral fractures, especially those occurring in the proximal region, present significant challenges in orthopedic care. These fractures often demand precise and stable fixation methods to promote optimal healing and restore function. The Proximal Femur Nail Antirotation (PFNA) is a sophisticated orthopedic implant designed to address these challenges by providing stable fixation while minimizing complications associated with femoral fractures.
Overview of PFNA
The PFNA is an intramedullary nail specifically designed for the fixation of proximal femoral fractures. Developed to address the limitations of earlier implants, PFNA incorporates advanced features to enhance stability and reduce the risk of complications. This device is particularly well-suited for treating pertrochanteric and subtrochanteric fractures, common among the elderly population.
Key Features of PFNA
Antirotation Mechanism: One of the standout features of PFNA is its antirotation mechanism. The nail is designed to resist rotational forces, providing increased stability at the fracture site. This is crucial for preventing malalignment and promoting optimal healing.
Anatomical Design: PFNA is anatomically contoured to closely match the shape of the proximal femur. This design minimizes stress concentrations and enhances load distribution, reducing the risk of complications such as implant loosening or breakage.
Material Composition: Typically constructed from titanium or titanium alloy, PFNA is known for its high strength and biocompatibility. The choice of materials ensures durability while minimizing the risk of adverse reactions in the patient.
Minimally Invasive Surgery: PFNA is often implanted through a minimally invasive procedure, reducing tissue damage and promoting quicker recovery. The smaller incision size contributes to lower infection rates and less postoperative pain.
Distal Locking Options: The nail features distal locking options to secure the implant in place, preventing migration and maintaining stability throughout the healing process.
Clinical Applications
PFNA is predominantly used in the treatment of pertrochanteric and subtrochanteric fractures, where stable fixation is crucial for optimal outcomes. Common clinical scenarios where PFNA may be employed include:
Intertrochanteric Fractures: PFNA is effective in managing fractures that occur between the greater and lesser trochanters. Its antirotation mechanism proves particularly beneficial in preventing complications associated with rotational instability.
Subtrochanteric Fractures: Subtrochanteric fractures, situated just below the lesser trochanter, often require robust fixation. PFNA's anatomical design and antirotation features make it a suitable choice for stabilizing fractures in this region.
Osteoporotic Fractures: Given the prevalence of osteoporosis in the elderly population, PFNA's design and material composition make it well-suited for providing stable fixation in patients with compromised bone quality.
Complications and Considerations
While PFNA is generally considered a reliable and effective implant, as with any medical intervention, there are potential complications to be aware of:
Infection: Despite the minimally invasive nature of the procedure, there is always a risk of infection. Proper aseptic techniques during surgery and postoperative care are crucial in minimizing this risk.
Implant Migration: Adequate fixation is essential to prevent implant migration. Careful surgical technique, correct nail length selection, and proper implant placement are critical factors in reducing the risk of migration.
Implant Breakage: Although rare, implant breakage can occur. Proper patient selection, meticulous surgical technique, and adherence to weight-bearing restrictions during the healing phase can help minimize this risk.
The Proximal Femur Nail Antirotation (PFNA) represents a significant advancement in the field of orthopedic surgery, specifically catering to the challenges associated with proximal femoral fractures. Its antirotation mechanism, anatomical design, and biocompatible materials make it a valuable tool in the hands of orthopedic surgeons aiming to achieve stable fixation and promote optimal healing. As technology and surgical techniques continue to evolve, PFNA stands as a testament to the ongoing pursuit of improved outcomes for patients with challenging femoral fractures.
Help us correct (or expand/improve) this article - Mail us your inputs at domore@alltraumaimplants.com
Related Articles
All About Cannulated Screws
Orthopedic Bone Plates: Types, Surgery, and FAQs
Understanding Osteosynthesis
Trauma Implants - A Comprehensive Guide
Titanium Orthopedic Implants: Revolutionizing Bone Surgery
Osteotomy of the Knee: Procedure, Recovery, and Considerations
Understanding Bipolar Hip Prosthesis
Proximal Femur Nail Antirotation (PFNA): Advancements in Femoral Fracture Fixation
You May Also Like
What is a Spinal Implant? Types, Usage and Options: A spinal implant is a device surgically placed into the spine to support and stabilize spinal bones, or to relieve nerve compression. They can be made of metal, plastic, or other materials and can include spinal fusion ... Read More
What are the types of orthopedic implants?: An orthopedic implant can be defined as a device which is manufactured to replace a joint, bone, or cartilage due to damage or deformity. You can distinguish the orthopedic implants by their type of material and the type of tissue it will replace ... Read More
Hip Prosthesis, Types of Hip Prostheses & Top Manufacturers: A hip prosthesis is a device that replaces a damaged hip joint. The hip consists of a convex femoral head inserted into a concave acetabulum within the pelvis, cushioned by articular cartilage within a synovial joint capsule. A hip prosthesis ... Read More
What are trauma implants? Materials used to make these implants: Mostly available in pure titanium (or titanium alloys such as Ti-6AI-4V or Ti-6AL-7Nb) and stainless steel, trauma implants are used in fixation of bone fractures. These implants may be further processed with ... Read More
Zimmer Biomet Names CEO of Dental/Spine Spin-Off: Zimmer Biomet Holdings, Inc. (NYSE and SIX: ZBH), a global leader in musculoskeletal healthcare, today announced that after an extensive search, Vafa Jamali has been appointed as CEO of "NewCo", the independent, publicly traded company that will be created by ... Read More
Bactiguard-coated Zimmer Biomet trauma implants receive European regulatory clearance: "I am very pleased that the CE mark has been secured for Bactiguard-coated Zimmer Biomet trauma implants. This clearance will pave the way for European market launch in 2021. At the same time, we are preparing for the submission of the U.S regulatory file ... Read More
A new non-surgical treatment to lessen patient’s pain and get them back to their active lifestyles: Miller Orthopedic Specialists introduces MOS Regenerative Medicine Solutions, a non-surgical treatment that uses a patient’s own stem cells to promote healing within. MOS Regenerative Medicine Solutions has multiple types of treatments that... Read More
Driving Orthopaedic Procedure Costs Down: OIC Launches One Procedure, One Price(TM) Initiative: In orthopaedic procedures, commoditized implants are typically the most significant expense. Medical devices companies have put exorbitant price tags on implants and tools differentiated by sales and marketing expenses, not innovative technology... Read More
Syntellix Lauded by Frost & Sullivan for its Bioresorbable Orthopedic Implant: The innovation reduces surgical complications and time in the OR without any major changes to standard procedures - all while decreasing healthcare costs. The MAGNEZIX implant's unique capability of converting metal to bone makes it an ideal implant of the future ... Read More
Trauma Implants Market to Reach 10.14 Billion by 2026: The global Trauma Implants Market size is expected to reach USD 10.14 billion by 2026, exhibiting a CAGR of 4.3% during the forecast period. The increasing prevalence of sports injuries among children and teenagers will contribute significantly to the Trauma Implants Market share in the forthcoming years... Read More
