All About Cannulated Screws: Function, Benefits, and Surgical Procedure
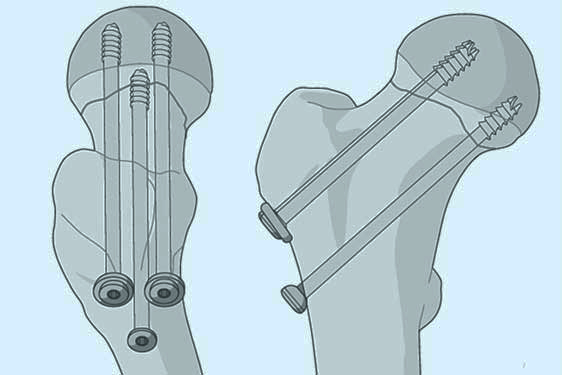
Cannulated Screws
Cannulated screws are medical devices commonly used in orthopedic surgeries for various applications. These screws have a hollow center, allowing for precise insertion over a guide wire. This feature makes them a versatile tool in the field of orthopedics, especially for stabilizing fractures and promoting bone healing. In this article, we will delve into the characteristics, functions, benefits, and the surgical process of inserting and, if necessary, removing cannulated screws.
What kind of device is a cannulated screw?
A cannulated screw is a specialized orthopedic implant designed for fixation in bone fractures. It is a type of screw with a hollow core, allowing for the insertion of a guide wire during surgery. These screws come in various lengths and diameters to accommodate different bone sizes and types of fractures.
Purpose of Cannulated Screws:
The primary purpose of cannulated screws is to stabilize fractures by providing internal fixation. They are commonly used in fractures of long bones, such as the femur, tibia, and humerus. Cannulated screws aid in maintaining the alignment of fractured bone fragments, promoting faster and more efficient healing. Additionally, they are utilized in arthrodesis procedures, where joint surfaces are fused to alleviate pain and improve joint function.
Benefits of Cannulated Screws:
a. Minimal Invasion: The hollow design allows for a less invasive surgical approach, reducing trauma to surrounding tissues.
b. Precise Placement: The insertion of cannulated screws is guided by a wire, ensuring accurate placement and alignment during surgery.
c. Enhanced Healing: Cannulated screws provide stable fixation, facilitating optimal conditions for bone healing.
d. Versatility: These screws can be used in various orthopedic procedures, making them a versatile tool for surgeons.
Diameter of Cannulated Screws:
Cannulated screws come in different diameters to accommodate the specific requirements of various surgical applications. The choice of diameter depends on factors such as the size and type of bone, as well as the nature of the fracture. The range typically varies from 2.0 mm to 7.0 mm or even larger, allowing surgeons to select the most suitable size for the given situation.
How are Cannulated Screws Inserted?
The surgical insertion of cannulated screws involves several steps:
a. Preoperative Planning: Surgeons assess the patient's condition, review imaging studies (X-rays, CT scans), and plan the surgery.
b. Anesthesia: The patient receives anesthesia to ensure comfort and pain control during the procedure.
c. Incision: A small incision is made over the fracture site to access the bone.
d. Guide Wire Insertion: A guide wire is carefully inserted through the hollow core of the cannulated screw, guiding its path during placement.
e. Screw Insertion: The cannulated screw is then threaded over the guide wire and precisely placed to stabilize the fracture.
f. Closure: The incision is closed, and the patient is monitored during the recovery period.
Do Cannulated Screws Get Removed?
In some cases, cannulated screws may be removed after the bone has sufficiently healed. This decision depends on factors such as the type of fracture, the location of the screw, and the patient's overall health. The removal process, known as screw extraction, is typically less complex than the initial insertion. It involves reopening the incision, locating the screw, and carefully extracting it, often with the aid of fluoroscopy or imaging.
Cannulated screws play a crucial role in orthopedic surgeries, offering surgeons a versatile and minimally invasive option for stabilizing fractures and promoting bone healing. The hollow design, precise placement, and various size options contribute to their widespread use in different orthopedic applications. Understanding the functions, benefits, and insertion procedures of cannulated screws provides valuable insights into their role in modern orthopedic practice.
Help us correct (or expand/improve) this article - Mail us your inputs at domore@alltraumaimplants.com
Related Articles
All About Cannulated Screws
Orthopedic Bone Plates: Types, Surgery, and FAQs
Understanding Osteosynthesis
Trauma Implants - A Comprehensive Guide
Titanium Orthopedic Implants: Revolutionizing Bone Surgery
Osteotomy of the Knee: Procedure, Recovery, and Considerations
Understanding Bipolar Hip Prosthesis
Proximal Femur Nail Antirotation (PFNA): Advancements in Femoral Fracture Fixation
You May Also Like
What is a Spinal Implant? Types, Usage and Options: A spinal implant is a device surgically placed into the spine to support and stabilize spinal bones, or to relieve nerve compression. They can be made of metal, plastic, or other materials and can include spinal fusion ... Read More
What are the types of orthopedic implants?: An orthopedic implant can be defined as a device which is manufactured to replace a joint, bone, or cartilage due to damage or deformity. You can distinguish the orthopedic implants by their type of material and the type of tissue it will replace ... Read More
Hip Prosthesis, Types of Hip Prostheses & Top Manufacturers: A hip prosthesis is a device that replaces a damaged hip joint. The hip consists of a convex femoral head inserted into a concave acetabulum within the pelvis, cushioned by articular cartilage within a synovial joint capsule. A hip prosthesis ... Read More
What are trauma implants? Materials used to make these implants: Mostly available in pure titanium (or titanium alloys such as Ti-6AI-4V or Ti-6AL-7Nb) and stainless steel, trauma implants are used in fixation of bone fractures. These implants may be further processed with ... Read More
Zimmer Biomet Names CEO of Dental/Spine Spin-Off: Zimmer Biomet Holdings, Inc. (NYSE and SIX: ZBH), a global leader in musculoskeletal healthcare, today announced that after an extensive search, Vafa Jamali has been appointed as CEO of "NewCo", the independent, publicly traded company that will be created by ... Read More
Bactiguard-coated Zimmer Biomet trauma implants receive European regulatory clearance: "I am very pleased that the CE mark has been secured for Bactiguard-coated Zimmer Biomet trauma implants. This clearance will pave the way for European market launch in 2021. At the same time, we are preparing for the submission of the U.S regulatory file ... Read More
A new non-surgical treatment to lessen patient’s pain and get them back to their active lifestyles: Miller Orthopedic Specialists introduces MOS Regenerative Medicine Solutions, a non-surgical treatment that uses a patient’s own stem cells to promote healing within. MOS Regenerative Medicine Solutions has multiple types of treatments that... Read More
Driving Orthopaedic Procedure Costs Down: OIC Launches One Procedure, One Price(TM) Initiative: In orthopaedic procedures, commoditized implants are typically the most significant expense. Medical devices companies have put exorbitant price tags on implants and tools differentiated by sales and marketing expenses, not innovative technology... Read More
Syntellix Lauded by Frost & Sullivan for its Bioresorbable Orthopedic Implant: The innovation reduces surgical complications and time in the OR without any major changes to standard procedures - all while decreasing healthcare costs. The MAGNEZIX implant's unique capability of converting metal to bone makes it an ideal implant of the future ... Read More
Trauma Implants Market to Reach 10.14 Billion by 2026: The global Trauma Implants Market size is expected to reach USD 10.14 billion by 2026, exhibiting a CAGR of 4.3% during the forecast period. The increasing prevalence of sports injuries among children and teenagers will contribute significantly to the Trauma Implants Market share in the forthcoming years... Read More
